1、读取HS3003温度传感器的数据
支持I2C接口的传感器种类有很多,本文对使用STM32U5的I2C读取NST112温湿度传感器的数据进行介绍。
2、
 硬件配置
硬件配置
本次使用一块扩展板上的NST112温度传感器作为硬件,温度传感器为纳芯微的NST112。
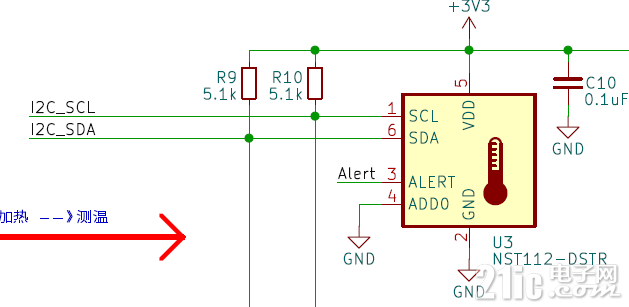
拓展板的界限引脚定义为和开发板与传感器器模块的接线图如图所示。
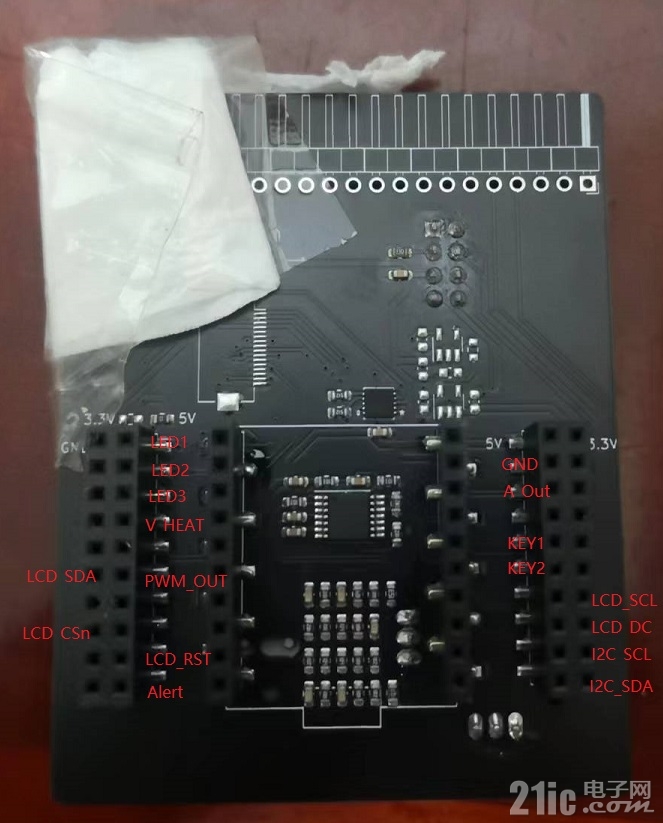
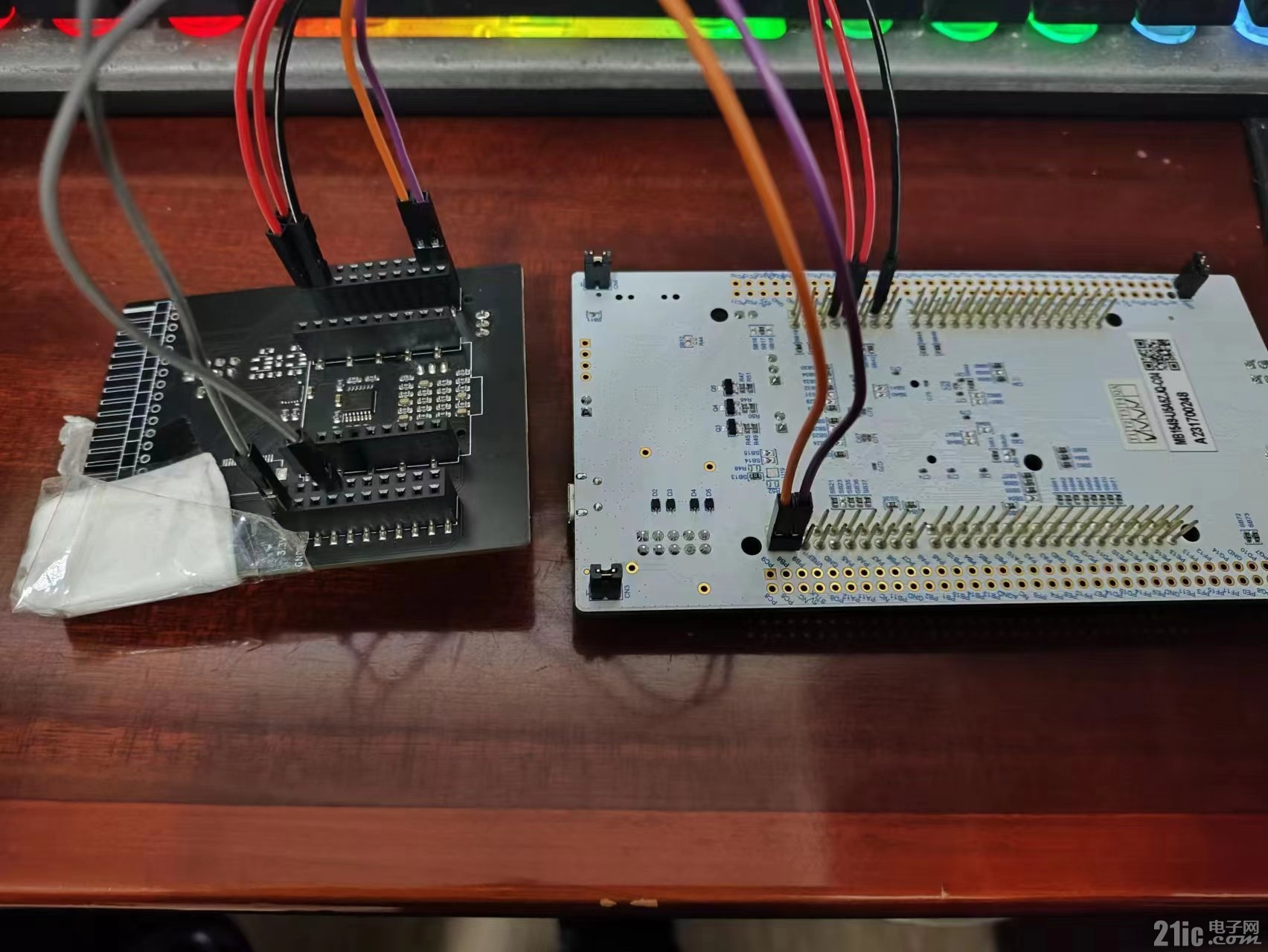
3、软件编写
首先,在STM32 CubeIDE中创建开发板的工程,选择根据开发板创建工程,
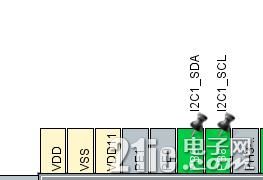
在CubeMX界面中会自动初始化开发板上的部分外设,比如串口、调试口、LED等,本文通过I2C1控制传感器,使用的PB8和PB9,选择对应管脚的复用功能,并在I2C的配置界面选择相应的I2C通讯参数。
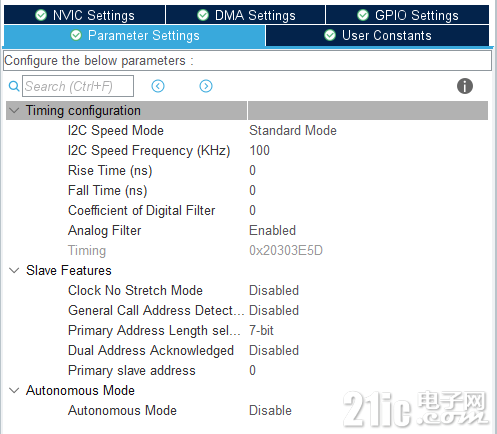
完成上述操作后,保存配置并生成相应的外设初始化代码。
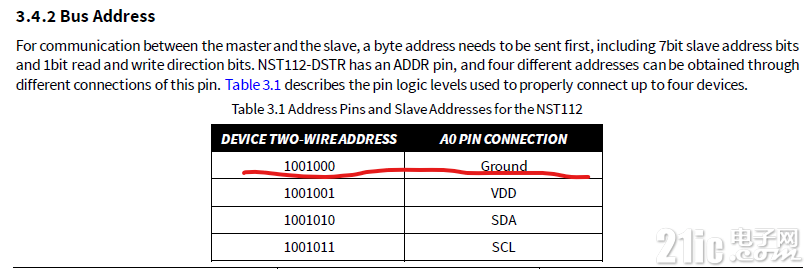
通过查看数据手册可知,ADD引脚的接线方式决定芯片的从机地址,结合原理图可知传感器的从机地址为0x48。
由于STM32 HAL接口的实现问题,在传入从机地址时,需要将第8位的读写控制位作为从机地址作为函数的参数传入。相关的宏定义如下
查看数据手册,可知NST112的寄存器一共有4个:配置寄存器、温度寄存器、温度上限寄存器以及温度下限寄存器。
在数据手册查看配置寄存器的介绍,在默认状态下,传感器工作在连续转换的工作模式下,转换分辨率为12位。
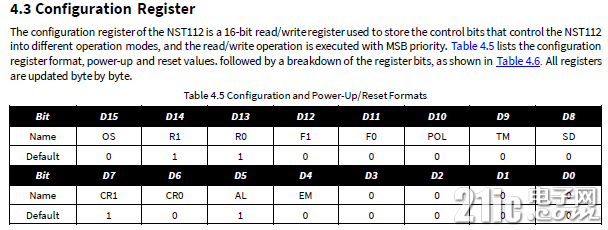
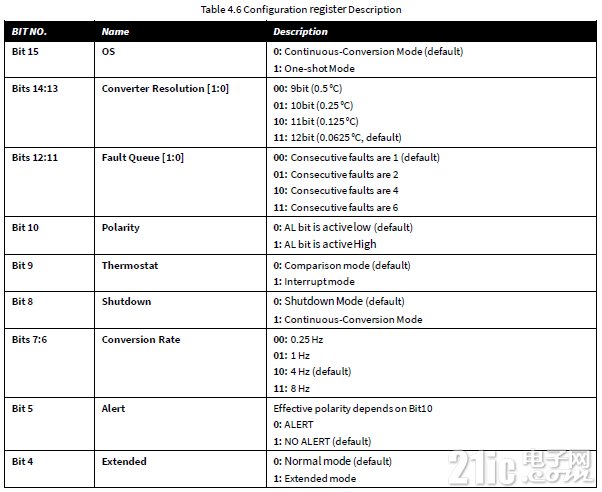
传感器中的寄存器的字长位16位,访问的时序如下图所示。
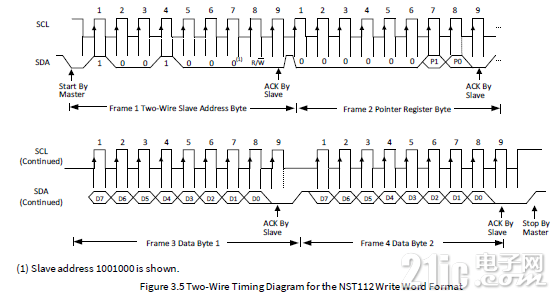
写操作的数据域为寄存器地址和两字节的数据,16位数据的高字节在前。
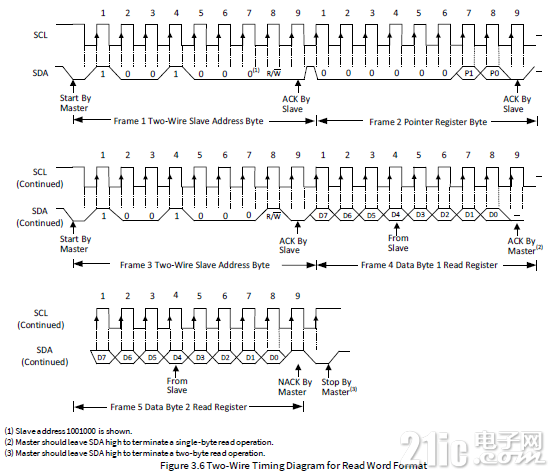
读操作的方式位,先写入寄存器地址,后进行读取。
综上,可以写出传感器寄存器的读写函数如下:
- void nst112_writeRegister( int reg_address, uint16_t val) {
- uint8_t ii[3]={0x00,0x00,0x00};
- ii[0] = reg_address;
- ii[1] = (uint8_t)((0xFF00 & val)>>8);
- ii[2] = (uint8_t)(0x00FF & val);
- if (HAL_I2C_Master_Transmit(&hi2c1, (uint16_t)NST112_I2C_ADDRESS_W, ii, 0x03,10000) != HAL_OK)
- {
- /* Error_Handler() function is called when error occurs. */
- Error_Handler();
- }
- /*##- Wait for the end of the transfer #################################*/
- /* Before starting a new communication transfer, you need to check the current
- state of the peripheral; if it�s busy you need to wait for the end of current
- transfer before starting a new one.
- For simplicity reasons, this example is just waiting till the end of the
- transfer, but application may perform other tasks while transfer operation
- is ongoing. */
- while (HAL_I2C_GetState(&hi2c1) != HAL_I2C_STATE_READY)
- {
- }
- }
- uint16_t nst112_readRegister(uint8_t reg_address) {
- uint16_t value=0;
- uint8_t temp[2]={0x00,0x00};
- if (HAL_I2C_Master_Transmit(&hi2c1, (uint16_t)NST112_I2C_ADDRESS_W, ®_address, 0x01,10000) != HAL_OK)
- {
- /* Error_Handler() function is called when error occurs. */
- Error_Handler();
- }
- /*##- Wait for the end of the transfer #################################*/
- /* Before starting a new communication transfer, you need to check the current
- state of the peripheral; if it�s busy you need to wait for the end of current
- transfer before starting a new one.
- For simplicity reasons, this example is just waiting till the end of the
- transfer, but application may perform other tasks while transfer operation
- is ongoing. */
- while (HAL_I2C_GetState(&hi2c1) != HAL_I2C_STATE_READY)
- {
- }
- /* Read data back from the I2C slave */
- if (HAL_I2C_Master_Receive(&hi2c1, (uint16_t)NST112_I2C_ADDRESS_R, temp, 0x02,10000) != HAL_OK)
- {
- /* Error_Handler() function is called when error occurs. */
- Error_Handler();
- }
- /*##- Wait for the end of the transfer #################################*/
- /* Before starting a new communication transfer, you need to check the current
- state of the peripheral; if it�s busy you need to wait for the end of current
- transfer before starting a new one.
- For simplicity reasons, this example is just waiting till the end of the
- transfer, but application may perform other tasks while transfer operation
- is ongoing. */
- while (HAL_I2C_GetState(&hi2c1) != HAL_I2C_STATE_READY)
- {
- }
- value=temp[0];
- value=value<<8;
- value=value | temp[1];
- return value;
- }
传感器在默认模式即可以实现温度检测,实现温度的读取,实际上只要实现读取温度寄存器值的函数即可。函数如下
- float nst112_readTemp(void) {
- uint16_t Origin_Temp = nst112_readRegister(TEMP_REG);
- float Temp=0;
- Temp = (char)(Origin_Temp>>8);
- unsigned char decimal=(unsigned char)Origin_Temp;
- if(Temp>=0){
- Temp += (float)(decimal>>4)/16;
- }
- else
- {
- Temp -= (float)(((~decimal)>>4)+1)/16;
- }
- return Temp;
- }
在主函数中调用以下函数
- while (1)
- {
- HAL_Delay(1000);
- Curr_Temp = nst112_readTemp();
- Chip_Config = nst112_getconfig();
- printf("global temp is %f\r\n",Curr_Temp);
- /* USER CODE END WHILE */
- /* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
- }
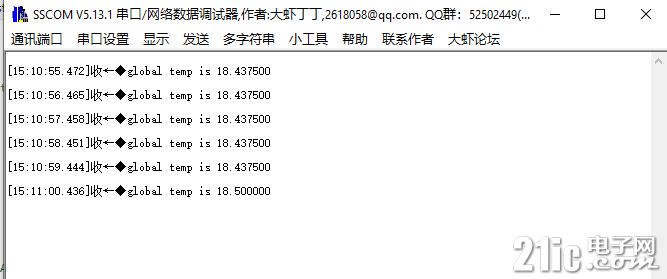
实际的温度通过串口打印效果如图。
4、总结
NST112温度寄存器的操作很简单,同时采集的数据为温度信息,在生活十分常见,很适合作为嵌入式入门的练手项目。
|