- #define SFUD_DEBUG_MODE
- #define SFUD_USING_SFDP
- #define SFUD_USING_FLASH_INFO_TABLE
- enum {
- SFUD_SPI_DEVICE_INDEX = 0,
- };
- #define SFUD_FLASH_DEVICE_TABLE \
- { \
- [SFUD_SPI_DEVICE_INDEX] = {.name = "ZD25Q80", .spi.name = "SPI1"}, \
- }
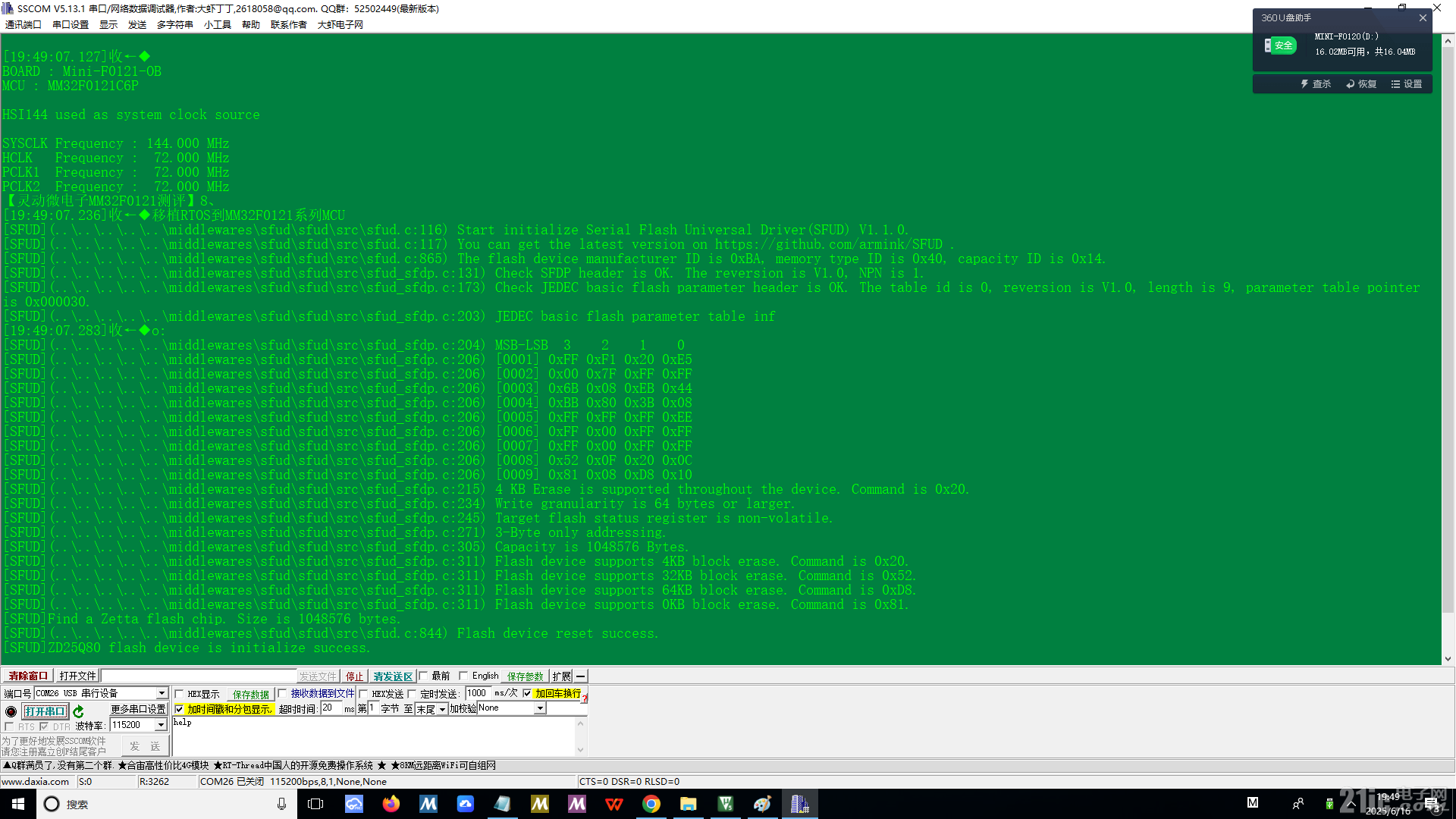
#define SFUD_MF_ID_ZETTA 0xBA
#define SFUD_FLASH_CHIP_TABLE \{ 其他flash {"ZD25Q80",SFUD_MF_ID_ZETTA,0x40,0x14,1L*1024L*1024L,SFUD_WM_PAGE_256B,4096,0x20}, \}
名字:"ZD25Q80"
珠海全志(Zetta)的典型ID:FUD_MF_ID_ZETTA(0xBA)
25Q80 类型编码:0x40
1MB容量编码(参考JEDEC):0x14
1MB:1 * 1024 * 1024
256字节页编程:SFUD_WM_PAGE_256B
4KB扇区擦除:4096
扇区擦除命令:0x20
sfud_port.c主要实现了SPI初始化、SPI发送接收函数spi_write_read,这是和SFUD的接口函数。
CS控制不能使用GPIO设置高低电平的方式,而要像下面这样写:
#define SPI_FLASH_CS_H() SPI_CSInternalSelected(SPI1, DISABLE)
#define SPI_FLASH_CS_L() SPI_CSInternalSelected(SPI1, ENABLE)- #include <sfud.h>
- #include <stdarg.h>
- #include "hal_conf.h"
- #include "sfud_cfg.h"
- #include "main.h"
- /* send dummy data for read data */
- #define DUMMY_DATA 0xFF
- extern uint32_t SystemCoreClock;
- static char log_buf[256u];
- void sfud_log_debug(const char *file, const long line, const char *format, ...);
- static void retry_delay_100us(void);
- static void spi_lock(const sfud_spi *spi)
- {
- __disable_irq();
- }
- static void spi_unlock(const sfud_spi *spi)
- {
- __enable_irq();
- }
- /* xfer data by spi port. */
- static uint8_t spi_xfer(const uint8_t value)
- {
-
- while (RESET == SPI_GetFlagStatus(SPI1, SPI_FLAG_TXEPT))
- {
- }
- SPI_SendData(SPI1, value);
- while (RESET == SPI_GetFlagStatus(SPI1, SPI_FLAG_RXAVL))
- {
- }
- return SPI_ReceiveData(SPI1);
- }
- /* control the cs pin output. */
- static void spi_cs_control(bool enable)
- {
- if (true == enable)
- {
- //GPIO_ResetBits(BOARD_FLASH_CS_GPIO_PORT, BOARD_FLASH_CS_GPIO_PIN);
- SPI_FLASH_CS_L();
-
- }
- else
- {
- //GPIO_SetBits(BOARD_FLASH_CS_GPIO_PORT, BOARD_FLASH_CS_GPIO_PIN);
- SPI_FLASH_CS_H();
- }
- }
- /**
- * SPI write data then read data
- */
- static sfud_err spi_write_read(const sfud_spi *spi, const uint8_t *write_buf, size_t write_size, uint8_t *read_buf,
- size_t read_size) {
- sfud_err result = SFUD_SUCCESS;
- uint32_t i;
- /* assert. */
- if (write_size)
- {
- SFUD_ASSERT(write_buf);
- }
- if (read_size)
- {
- SFUD_ASSERT(read_buf);
- }
- /* CS Pin valid. */
- spi_cs_control(true);
- /* put data. */
- for (i = 0u; i < write_size; i++)
- {
- spi_xfer(write_buf[i]);
- }
- /* recv data. */
- for (i = 0u; i < read_size; i++)
- {
- read_buf[i] = spi_xfer(DUMMY_DATA);
- }
- /* CS Pin invalid. */
- spi_cs_control(false);
- return result;
- }
- void SPI_Configure(void)
- {
- GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct;
- SPI_InitTypeDef SPI_InitStruct;
- RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_SPI1, ENABLE);
- SPI_StructInit(&SPI_InitStruct);
- SPI_InitStruct.SPI_Mode = SPI_Mode_Master;
- SPI_InitStruct.SPI_DataSize = SPI_DataSize_8b;
- SPI_InitStruct.SPI_DataWidth = 8;
- SPI_InitStruct.SPI_CPOL = SPI_CPOL_Low;
- SPI_InitStruct.SPI_CPHA = SPI_CPHA_1Edge;
- SPI_InitStruct.SPI_NSS = SPI_NSS_Soft;
- SPI_InitStruct.SPI_BaudRatePrescaler = SPI_BaudRatePrescaler_256;
- SPI_InitStruct.SPI_FirstBit = SPI_FirstBit_MSB;
- SPI_Init(SPI1, &SPI_InitStruct);
- SPI_BiDirectionalLineConfig(SPI1, SPI_Enable_RX);
- SPI_BiDirectionalLineConfig(SPI1, SPI_Enable_TX);
- RCC_AHBPeriphClockCmd(RCC_AHBPeriph_GPIOA, ENABLE);
- GPIO_PinAFConfig(GPIOA, GPIO_PinSource4, GPIO_AF_0);
- GPIO_PinAFConfig(GPIOA, GPIO_PinSource5, GPIO_AF_0);
- GPIO_PinAFConfig(GPIOA, GPIO_PinSource6, GPIO_AF_0);
- GPIO_PinAFConfig(GPIOA, GPIO_PinSource7, GPIO_AF_0);
- GPIO_StructInit(&GPIO_InitStruct);
- GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_4 | GPIO_Pin_5 | GPIO_Pin_7;
- GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_High;
- GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP;
- GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStruct);
- GPIO_StructInit(&GPIO_InitStruct);
- GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_6;
- GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_High;
- GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_IPU;
- GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStruct);
- SPI_Cmd(SPI1, ENABLE);
- }
- sfud_err sfud_spi_port_init(sfud_flash *flash)
- {
- sfud_err result = SFUD_SUCCESS;
- /* Setup SPI module. */
- SPI_Configure();
- /* init sfud spi obj. */
- flash->spi.wr = spi_write_read;
- flash->spi.lock = spi_lock;
- flash->spi.unlock = spi_unlock;
- flash->spi.user_data = NULL;
- flash->retry.delay = retry_delay_100us;
- flash->retry.times = 60u * 10000u;
- return result;
- }
- /**
- * This function is print debug info.
- *
- * @param file the file which has call this function
- * @param line the line number which has call this function
- * @param format output format
- * @param ... args
- */
- void sfud_log_debug(const char *file, const long line, const char *format, ...)
- {
- va_list args;
- /* args point to the first variable parameter */
- va_start(args, format);
- printf("[SFUD](%s:%ld) ", file, line);
- /* must use vprintf to print */
- vsnprintf(log_buf, sizeof(log_buf), format, args);
- printf("%s\r\n", log_buf);
- va_end(args);
- }
- /**
- * This function is print routine info.
- *
- * @param format output format
- * @param ... args
- */
- void sfud_log_info(const char *format, ...)
- {
- va_list args;
- /* args point to the first variable parameter */
- va_start(args, format);
- printf("[SFUD]");
- /* must use vprintf to print */
- vsnprintf(log_buf, sizeof(log_buf), format, args);
- printf("%s\r\n", log_buf);
- va_end(args);
- }
- static void retry_delay_100us(void)
- {
- uint32_t i;
- for ( i = 0; i < SystemCoreClock / 10000u; i++)
- {
- __NOP();
- }
- }
2、littlefs接口文件
lfs_port.c需要实现几个接口函数,需要注意lfs_flash_init中的参数与flash的参数相对应- #include "lfs.h"
- #include "sfud.h"
- int lfs_flash_init( struct lfs_config *c);
- static int lfs_flash_read(const struct lfs_config *c, lfs_block_t block, lfs_off_t off, void *buffer, lfs_size_t size);
- static int lfs_flash_prog(const struct lfs_config *c, lfs_block_t block, lfs_off_t off, const void *buffer, lfs_size_t size);
- static int lfs_flash_erase(const struct lfs_config *c, lfs_block_t block);
- static int lfs_flash_sync(const struct lfs_config *c);
- int lfs_flash_init(struct lfs_config *c)
- {
- sfud_init(); /* init sfud. */
- const sfud_flash *flash = sfud_get_device(0u);
- c->read = lfs_flash_read;
- c->prog = lfs_flash_prog;
- c->erase = lfs_flash_erase;
- c->sync = lfs_flash_sync;
- c->read_size = 16;
- c->prog_size = 256;//16;
- //c->block_size = LFS_FLASH_SECTOR_SIZE;
- c->block_size = 4096;//flash->chip.erase_gran;
- c->block_count = 256;
- c->block_cycles = 500;
- c->cache_size = 256;//16;
- c->lookahead_size = 16;
- //c->read_buffer = (void *)lfs_flash_read_buf;
- //c->prog_buffer = (void *)lfs_flash_prog_buf;
- //c->lookahead_buffer = (void *)lfs_flash_lookahead_buf;
- return LFS_ERR_OK;
- }
- static int lfs_flash_read(const struct lfs_config *c, lfs_block_t block, lfs_off_t off, void *buffer, lfs_size_t size)
- {
- uint32_t addr = block * c->block_size + off;
- const sfud_flash *flash = sfud_get_device(0u);
- sfud_read(flash, addr, size, (uint8_t *)buffer);
- return LFS_ERR_OK;
- }
- static int
- lfs_flash_prog(const struct lfs_config *c, lfs_block_t block, lfs_off_t off, const void *buffer, lfs_size_t size)
- {
- uint32_t addr = block * c->block_size + off;
- const sfud_flash *flash = sfud_get_device(0u);
- sfud_write(flash, addr, size, (uint8_t *)buffer);
- return LFS_ERR_OK;
- }
- static int lfs_flash_erase(const struct lfs_config *c, lfs_block_t block)
- {
- const sfud_flash *flash = sfud_get_device(0u);
- sfud_erase(flash, block * c->block_size, c->block_size);
- return LFS_ERR_OK;
- }
- static int lfs_flash_sync(const struct lfs_config *c)
- {
- return LFS_ERR_OK;
- }
3、写一个测试函数- void lfsTask(void *pvParameters )
- {
- int err = lfs_flash_init(&app_lfs_config);
- if (err)
- {
- printf("lfs_flash_init() failed.\r\n");
- while (1);
- }
-
- err = lfs_mount(&app_lfs, &app_lfs_config);
- if (err)
- {
- printf("lfs_mount() failed.\r\n");
- lfs_format(&app_lfs, &app_lfs_config);
- printf("lfs_format() done.\r\n");
- lfs_mount(&app_lfs, &app_lfs_config);
- printf("lfs_mount() done.\r\n");
- }
-
- // read current count
- uint32_t boot_count = 0;
- lfs_file_open(&app_lfs, &app_lfs_file, "boot_count", LFS_O_RDWR | LFS_O_CREAT);
- lfs_file_read(&app_lfs, &app_lfs_file, &boot_count, sizeof(boot_count));
- // update boot count
- boot_count += 1;
- lfs_file_rewind(&app_lfs, &app_lfs_file);
- lfs_file_write(&app_lfs, &app_lfs_file, &boot_count, sizeof(boot_count));
- // remember the storage is not updated until the file is closed successfully
- lfs_file_close(&app_lfs, &app_lfs_file);
- // release any resources we were using
- lfs_unmount(&app_lfs);
-
-
- for( ;; )
- {
- // print the boot count
- printf("boot_count: %u\r\n", (unsigned)boot_count);
- vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(2000));
- }
- }