本帖最后由 forgot 于 2023-8-29 08:44 编辑
IEEE-802.11be-QSDK-IIOT-IPQ9574-IPQ9554-QCN9274-QCN6274-Throughput 30Gbps-4096-QAM-16x16 MIMO
WiFi 7 has become one of the hottest topics, especially after Qualcomm, H3C and other manufacturers released WiFi 7 commercial solutions, the discussion about WiFi 7 exploded again. So, what are the significant improvements in WiFi 7 compared to WiFi 6?
Now many wireless companies are preparing to develop and produce WiFi7 products, but most companies choose the following chips, IPQ9574-IPQ9554, these two chips are mainly used for the CPU of the motherboard, QCN9274-QCN6274, everyone knows, QCN The series are mainly used for the CPU of WiFi moudle, and the specifications designed by each company are different.
As one of the companies, Wallys uses IPQ9574 as the CPU in the mainboard design, and the mainboard design is 4x4 2.4G, supporting 4 M.2 WiFi7 moudles to meet customers’ needs for more radios
QCN9274-QCN6274 is the main chip of WiFi7 moudle, and each company designs differently. Wallys designs many versions, such as 4x4 single-frequency card and 2x2 dual-frequency card, to meet the needs of different customers for lines.
First of all, the wireless transmission rate of WiFi 7 has been greatly improved, jumping from 9.6Gbps of WiFi 6 to 30Gbps. This is mainly due to the expansion of frequency bands and wireless channels, as well as the upgrade of modulation methods.

There are many WiFi technologies improved by WiFi7, which will be used in more industrial projects:
1. According to the IEEE standard, wifi7 uses 802.11be. And wifi6 uses 802.11ax.
2. In terms of maximum transmission rate, wifi7 has a rate of 30Gbps, which is a huge improvement compared to 9.6Gpbs of wifi6.
3. In terms of bandwidth, wifi7 can reach up to 320MHz, which is twice the size of wifi6 up to 160MHz.
The goal of the Wi-Fi 7 protocol is to increase the throughput rate of the WLAN network to 30Gbps and provide low-latency access guarantees. In order to meet this goal, the entire protocol has made corresponding changes in the PHY layer and MAC layer.
The license-free spectrum in the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands is limited and crowded. When existing Wi-Fi runs emerging applications such as VR/AR, it will inevitably encounter the problem of low QoS. In order to achieve the goal of a maximum throughput of no less than 30Gbps, Wi-Fi 7 will continue to introduce the 6GHz frequency band and add new bandwidth modes, including continuous 240MHz, non-continuous 160+80MHz, continuous 320 MHz and non-continuous 160+160MHz.
4. In terms of modulation, the 4096-QAM of wifi7 can adapt to stronger transmission changes than the 1024-QAM of wifi6.
Wi-Fi 7 will introduce 4096-QAM, so that the modulation symbols carry 12 bits. Under the same encoding, Wi-Fi 7's 4096-QAM can achieve a 20% rate increase compared to Wi-Fi 6's 1024-QAM.
5. In terms of MIMO, wifi7 has been increased from 8x8 of wifi6 to 16x16, which will be able to support signal interconnection of more devices and base stations.
In Wi-Fi 7, the number of spatial streams has been increased from 8 to 16 in Wi-Fi 6, which theoretically can more than double the physical transmission rate. Supporting more data streams will also bring more powerful features-distributed MIMO, which means that 16 data streams can be provided not by one access point, but by multiple access points at the same time, which means multiple APs need to cooperate with each other to work.
6. Support cooperative scheduling among multiple APs
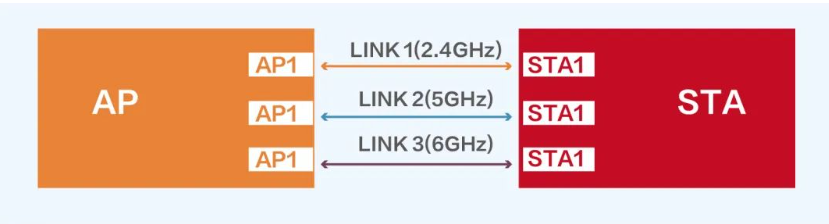
Currently, within the framework of the 802.11 protocol, there is actually not much cooperation between APs. Common WLAN functions such as automatic tuning and smart roaming are vendor-defined features. The purpose of inter-AP cooperation is only to optimize channel selection, adjust the load among APs, etc., so as to achieve the purpose of efficient utilization and balanced allocation of radio frequency resources. Coordinated scheduling between multiple APs in Wi-Fi 7, including coordinated planning between cells in the time domain and frequency domain, interference coordination between cells, and distributed MIMO, can effectively reduce the interference between APs, greatly Improve the utilization of air interface resources.
There are many ways to coordinate scheduling between multiple APs, including C-OFDMA (Coordinated Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access), CSR (Coordinated Spatial Reuse), CBF (Coordinated Beamforming), and JXT (Joint Transmission).
7. Multiple resource unit, MRU (Multiple resource uint), is a technology to improve the utilization rate of spectrum resources.
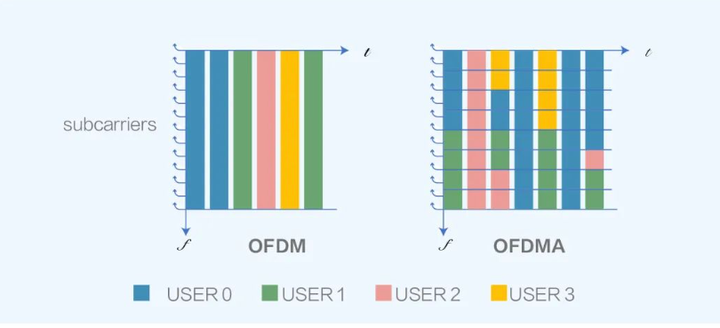
The number of subcarriers contained in an RU is not randomly combined. The Wi-Fi standard specifies the fixed combination form of RU, mainly: 26-tone RU (that is, 26 subcarriers form one RU), 52-tone RU, 106-tone RU, 242-tone RU, 484-tone RU, 996-tone RU, 1992-tone RU.
In Wi-Fi 6, a user can only correspond to one RU. Wi-Fi 7 proposes the MRU concept, where a user can be allocated multiple RUs.
So what is the use of this MRU?
For example, a 20MHz channel should be used by 3 users. In Wi-Fi 6, the allocation of the maximum resource utilization is as follows: 1 user is allocated 106-tone RU, 2 users are allocated 52-tone RU respectively, a total of 210 subcarriers (tones) are shared, and 24 subcarriers are wasted (A 20MHz channel has a total of 234 effective subcarriers.
Now, with Wi-Fi 7 applying MRU, one user can be allocated 106-tone RU+26-tone RU (two RUs are allocated to one user), and the other two users can still be allocated 52-tone RU respectively. In this way, the resources of the 20MHz channel are fully used, the utilization rate of channel resources is improved, the rate is increased, and the delay is reduced.
It should be noted that not any two RUs can form an MRU, but there are limited conditions. The Wi-Fi 7 standard divides RUs into two categories: small RUs and large RUs. It stipulates that only RUs in the same category can be combined into one MRU, that is, they must be both small RUs or large RUs. Only then can an MRU be formed.
Small RU: 26-tone RU, 52-tone RU, 106-tone RU,
Most RUs: 242-tone RU, 484-tone RU, 996-tone RU, 1992-tone RU
Application Scenarios of Wi-Fi 7
The new features introduced by Wi-Fi 7 will greatly increase the data transmission rate and provide lower latency, and these advantages will be more helpful to emerging applications, as follows:
video stream,
Video/Voice Conferencing
wireless gaming
real-time collaboration
Cloud/Edge Computing
Industrial Internet of Things
Immersive AR/VR
interactive telemedicine
|
|